Science class 8
Of science chapter 👇👇.
THE CELL : ITS FUNCTIONS AND STRUCTURE
Notes
- Cell is the basic structural as well as functional unit of all living organisms.
- Discovery of cell - 1. Robert Hooke was the first scientists who observed thin slices of cork in 1665 by microscope which was designed by him. 2. In Latin cell means 'a little room' .
- On the basis of ' number of cells', living organisms are divided into two categories: Unicellular and Multicellular.
- Example of unicellular- Euglena,Amoeba,Paramoecium.
- Example of multicellular- Humans,Birds,Animals.
- There are many different shapes of cell.
- Smallest cell PPLO ( Pleural pneumonia - like organism) also called Mycoplasma is about 0.1 micron.
- Ostrich egg is considered as largest cell is (nearly) 170mm in diameter.
- μ= 0.1 micron
- 0.1 micron = 10^-6
- μm = micron meter
- mm = milimeter
- 1μ = 10^-3 mm
- 10^-6 m = 10^-3mm CELL SIZE
- Amoeba 1000 μm
- Hen's egg 60mm
- Ostrich egg 170 mm
- Green laga, Chara 10 cm CELL OF HUMAN BODY SIZE
- Red blood cell 9 μm
- Liver cell 20 μm
- Human Ovum 0.1 mm
- Nerve cell About 1m
- Life span of RBCs is about 120 days.
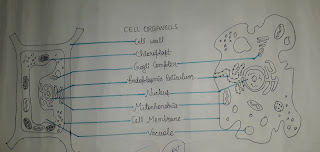
- Parts of cell- 1. Cell membrane 2. Cytoplasm 3. Nucleus 4. Cell organelles
- Cell membrane - All living cells are bound by a membrane called the plasma membrane, or cell membrane. It surrounds its inner gel- like material called protoplasma. The Cell of plants, fungi and bacteria have an additional outer covering called cell wall. Cell membrane controll enter and exit substance in the cell. Cell wall provide rigidity to cell.
- Cytoplasm - The portion of the cell membrane is called cytoplasm. [Kytos ( hollow) , plasma (liquid)]. It acts as ground substance.
- Nucleus - The nucleus is a dense structure bound by a nucleus membrane. The protoplasma of the nucleus is called nucleoplasm. It has a thread like network called chromatin. When cell is ready to divide this chromatin condenses to form thicker, thread - like structure , called chromosomes. Organism Chromosome no.
- Man 46
- Dog 78
- Pigeon 80
- Wheat 42
- Yeast 32
- Nucleus is the brain of the cell.
- Cell organelles 1. Plastids - ● Chloroplast ● Chromoplast ● Leucoplasts ■ Chloroplast are green coloured plastids. It has chlorophyll which help in photosynthesis. ■ Chromoplast give colours to fruit. ■ Leucoplasts is colourless. It provide space for containing starch. 2. Mitochondria - It is known as power house of cell. 3. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) - It provide channels for transport. ● Rough (ER) ● Smooth (ER) ■ Rough (ER) - It plays a vital role in synthesis of protein. ■ Smooth (ER) - It helps in synthesis of fats. 4. Gogli Complex - They are involved in processing and packing of materials produce by cell. 5. Vacuole - It stores excess water and wastes product. 6. Ribosomes - They help in protein synthesis. 7. Cillia and flagella - They help in locomotion and collection of food.
- LEVEL OF ORANNISATION IN AN ORGANISMS IN ASCENDING ORDER - Cell , Tissue ,Organ , Organ system , Organism
- DIFFERENCE BETWEEN PLANT AND ANIMAL CELL Character Plant cell Animal cell
- Shape Fixed Not Fixed
- Cell wall Present Absent
- Plastids Present Absent
- Vacoules One large Vacoules are vacoules is either absent, present. or are present only as small vacoules.


Comments
Post a Comment